™Here’s why leafy greens should be at the top of your dietary list for bone health:
1. Calcium-Rich Goodness
While dairy products are known for their calcium content, green leafy vegetables can be just as potent. Calcium is a fundamental mineral for bone health, and leafy greens like kale, collard greens, and turnip greens provide an excellent plant-based source of this nutrient. One cup of cooked kale can offer as much calcium as a cup of milk, making it an essential addition to your diet.
2. Vitamin K: The Bone Protector
Leafy greens are rich in vitamin K, a nutrient vital for bone health. Vitamin K helps in the activation of osteocalcin, a protein that binds calcium to the bone matrix, strengthening bones. Additionally, vitamin K helps reduce excessive bone demineralization, protecting against bone loss and fractures. Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are particularly high in vitamin K, making them superstars for your skeletal system.
3. Magnesium for Bone Metabolism
Magnesium is another crucial nutrient found abundantly in leafy greens. About 50-60% of the body’s magnesium is stored in the bones, where it plays a pivotal role in bone metabolism and mineralization. Magnesium also assists in converting vitamin D into its active form, which aids in calcium absorption. Incorporating greens like spinach and kale into your diet ensures you get enough magnesium for optimal bone health.
4. Maintaining Alkaline Balance
A diet rich in leafy greens helps maintain the body’s acid-base balance, which is essential for bone health. When the body becomes too acidic, it may leach calcium from the bones to neutralize the acid, leading to weakened bones. Leafy greens, being alkaline, help maintain a balanced pH, preventing calcium loss and keeping your bones strong and healthy.
5. Packed with Antioxidants and Other Nutrients
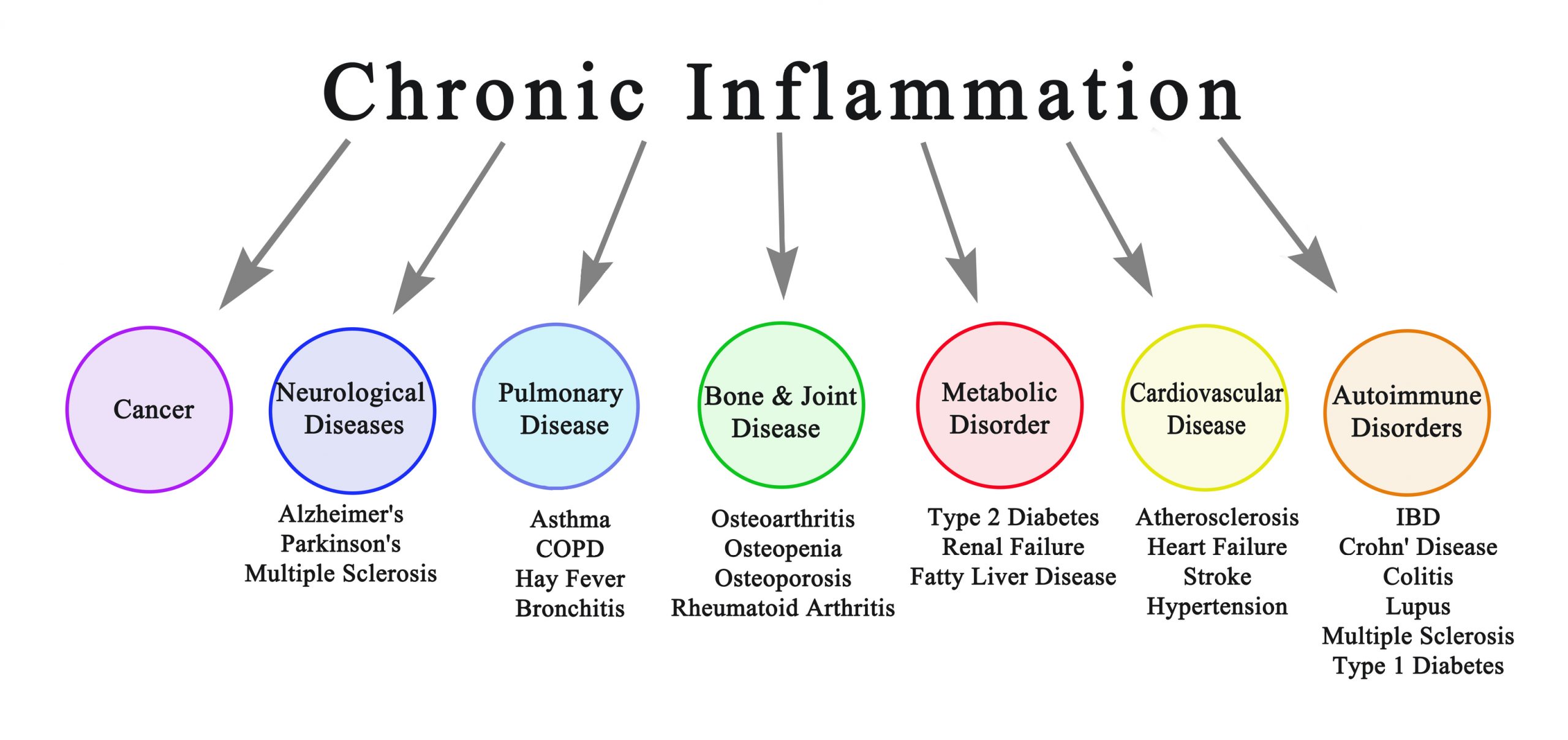
Green leafy vegetables are packed with a range of vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health. Vitamin C, found in greens like kale and spinach, is necessary for collagen formation, which is a critical component of bone structure. Additionally, the antioxidants in leafy greens help protect bone cells from damage and reduce inflammation. The concept of osteoimmunology highlights the connection between the immune system and bone health. Nutrients found in leafy greens help modulate immune responses, reducing inflammation and promoting bone regeneration and repair.
6. Fiber for Digestive Health
Leafy greens are high in dietary fiber, which supports a healthy digestive tract and promotes regular bowel movements. Fiber also aids in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for bone health. A healthy gut microbiome can enhance nutrient absorption, including calcium and magnesium, synthesize essential vitamins such as vitamin K2, reduce inflammation, and regulate hormones, all of which further support bone health.
I recommend aiming to get 2-3 cups of leafy greens a day
Practical Ways to Add Leafy Greens to Your Diet
1. Smoothies: Add a handful of your favorite greens to your smoothie.
2. Salads: Make leafy greens the base of your salads. Mix varieties like arugula, romaine, kale, and spinach for a nutrient-packed meal.
3. Soups and Stews: Add chopped greens to soups, stews, and broths. They add flavor and a nutritional boost.
4. Stir-Fries: Incorporate greens like bok choy or Swiss chard into your stir-fries for a quick and healthy dinner.
5. Wraps and Sandwiches: Use large leafy greens as wraps or add them to sandwiches for extra crunch and nutrition.
NOTE: While green leafy vegetables are incredibly beneficial for bone health and overall well-being, it is important to be mindful of their oxalate content. Oxalates, are naturally occurring compounds found in many plants, including leafy greens, nuts, seeds and certain vegetables. They can bind to minerals in the gut which can interfere with their absorption. For this reason, oxalates are considered anti-nutrients. I delve deeper into the topic of oxalates in my BONES Method™ Program where I discuss what foods have the highest oxalate content, the best alternatives, and how to manage oxalate intake effectively. Supporting optimal bone health doesn’t require perfection—it requires balance. In this program you will discover how a well-rounded, nutritious diet can contribute to strong bones and overall wellness.
CLICK HERE to learn more about my program.
Incorporating green leafy vegetables into your daily diet is a simple and effective way to support your bone health. These greens provide a rich source of calcium, vitamin K, magnesium, fiber, and antioxidants, all of which are essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones. Additionally, their benefits extend to supporting digestive health and boosting immune function, making them a cornerstone of a bone-healthy diet. So next time you plan your meals, make sure to include a generous serving of leafy greens and give your bones the nourishment they need to stay strong for life.
Eat like a horse, and enjoy the benefits of strong, healthy bones for years to come!