by Susan Brady | Jul 23, 2021 | Digestion

Chronic, systemic inflammation is the type of inflammation that lingers on in the body and damages our cells and our tissues. It can play a huge role in numerous health conditions from cardiovascular disease to diabetes, cancers, and even osteoporosis. Luckily, there are things you can do to put out the fire!
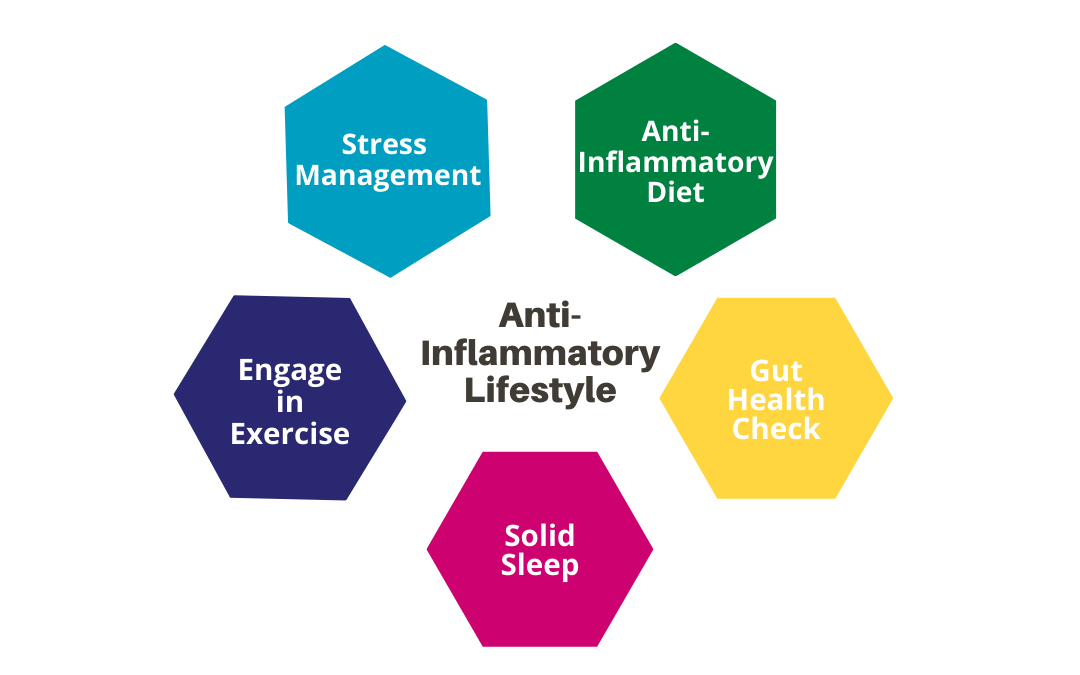
5 Steps to Dousing the Flames
1. Flip the Switch on Stress
One thing that causes inflammation is chronic emotional stress. When we are stressed out it activates our sympathetic nervous system. Our sympathetic nervous system is known as our fight or flight nervous system. When it becomes activated, our body thinks that we are under attack. The sympathetic nervous system revs up our system to get it ready to either fight off the attack or run from it. And one of the ways that it revs up our system is to produce cortisol and other inflammatory proteins. These chemicals are beneficial when we are experiencing short-term stress. However, if they linger as they do with chronic, ongoing stress, they can damage the body and create systemic inflammation.
Having a toolbox of stress-reducing techniques can flip the switch on stress and bring calm to the system. The mind-body techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, meditation, Yoga, have all been demonstrated to have a powerful effect for reducing mental stress and relieving inflammatory conditions. My go-to when I am feeling stressed is deep breathing, especially deep breathing with a very slow exhalation. Deep breathing helps to stimulate the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve runs from the brain through the neck and chest area and down to the abdomen and helps to regulate digestion, heart rate, and respiratory rate. When you stimulate the vagus nerve through deep breathing it can lower your heart rate, lower blood pressure, helps to regulate cortisol levels, and suppress inflammation. We are all faced with stress, and that’s not going to change, but what can change is having ways to handle the stress so it doesn’t become chronic and damaging.
2. Engage in Exercise
Exercise also helps to decrease inflammation. As reported in ScienceDaily, a study published in the journal Brain, Behavior and Immunity showed that as little as 20 minutes of exercise reduces inflammation. The exercise doesn’t need to be intense and even 20 minutes of moderate exercise, like walking, can have anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, regular exercise helps to reduce stress as well as fat mass. Fat, especially abdominal fat, produces inflammatory proteins that contribute to systemic inflammation. Any activity that reduces abdominal fat will reduce systemic inflammation.
3. Get some Solid Sleep
There is a lot of strong evidence that shows a lack of sleep raises levels of inflammation in the body. In fact, a study published back in 2010 revealed that people who sleep poorly or don’t get enough sleep to have higher levels of inflammation. Try your best to get between 7-9 hours of sleep at night. If you struggle with sleep, reach out to your health care practitioner to explore ways to help you get a better night’s sleep.
4. Get your Gut Checked
Another important issue when it comes to combating systemic inflammation is gut health. Digestive and gut dysfunction is one of the greatest contributors to chronic inflammation. Conditions like leaky gut and gut dysbiosis have far-reaching effects throughout the body, from your brain to your bones. If you have symptoms of gas, bloating, indigestion, chronic constipation, brain fog, mood issues, or joint and muscle aches and pains, please get your gut checked.
5. Follow an Anti-inflammatory Diet
Following an anti-inflammatory diet can help support healing if inflammation already exists as well as prevent chronic inflammation in the future. You have to avoid heavily processed, packaged foods with salt and sugar and refined carbohydrates, and pro-inflammatory vegetable oils like corn, sunflower, safflower, and soy. All of these types of food will fuel inflammation.
An anti-inflammatory diet is rich in vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, whole grains, and fatty fish. Some of the top vegetables and fruits for reducing inflammation are green leafy vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, garlic, onions, and fruits such as citrus fruits and berries. It is really important to get enough omega 3 fatty acids from foods like wild-caught salmon or sardines as well as flax seeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. There are also many wonderful anti-inflammatory herbs like turmeric, ginger, rosemary, sage, oregano, and cinnamon that can be used to spice up your meals and turn down the heat.
Click Here for a complete guide to the Anti-Inflammatory diet.
Following these lifestyle principles will help to heal and prevent systemic inflammation that can contribute to disease, aging, and osteoporosis.
If you are interested to see if inflammation may be contributing to your health issues, I would recommend filling out the Inflammatory Index Questionnaire to get a baseline of your symptoms. Then after following the principles of an anti-inflammatory lifestyle for several months, retake the questionnaire to see how your symptoms have changed.
Click Here for the Inflammatory Index Questionnaire
Please reach out if I can help you!

by Susan Brady | Jul 19, 2021 | Digestion

Seven Consequences of Chronic Inflammation
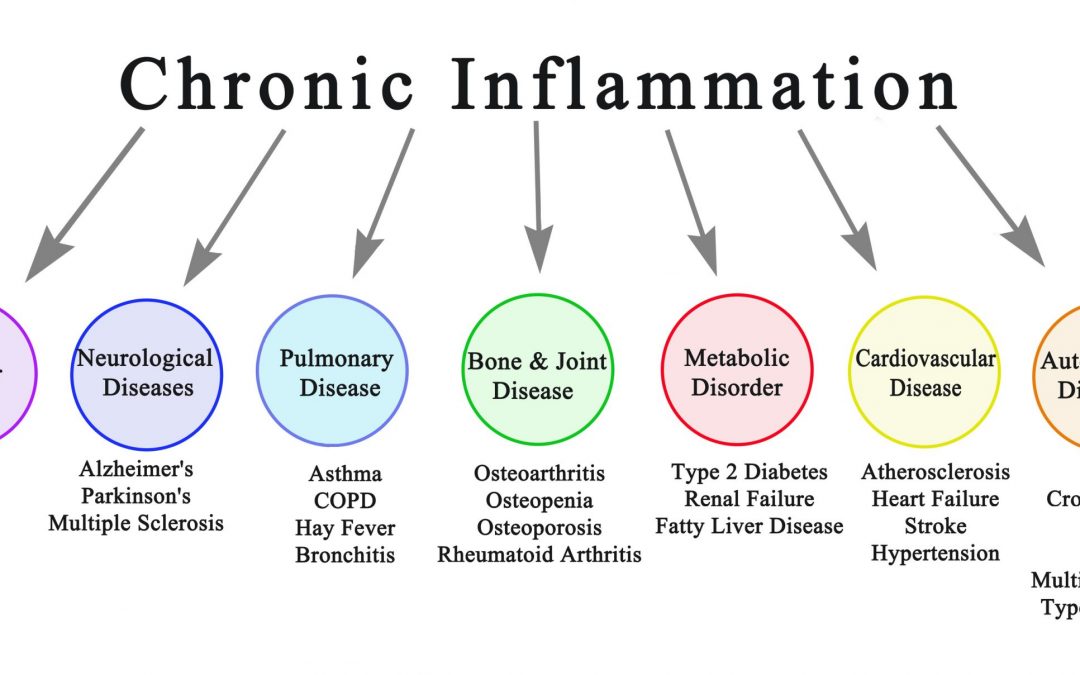
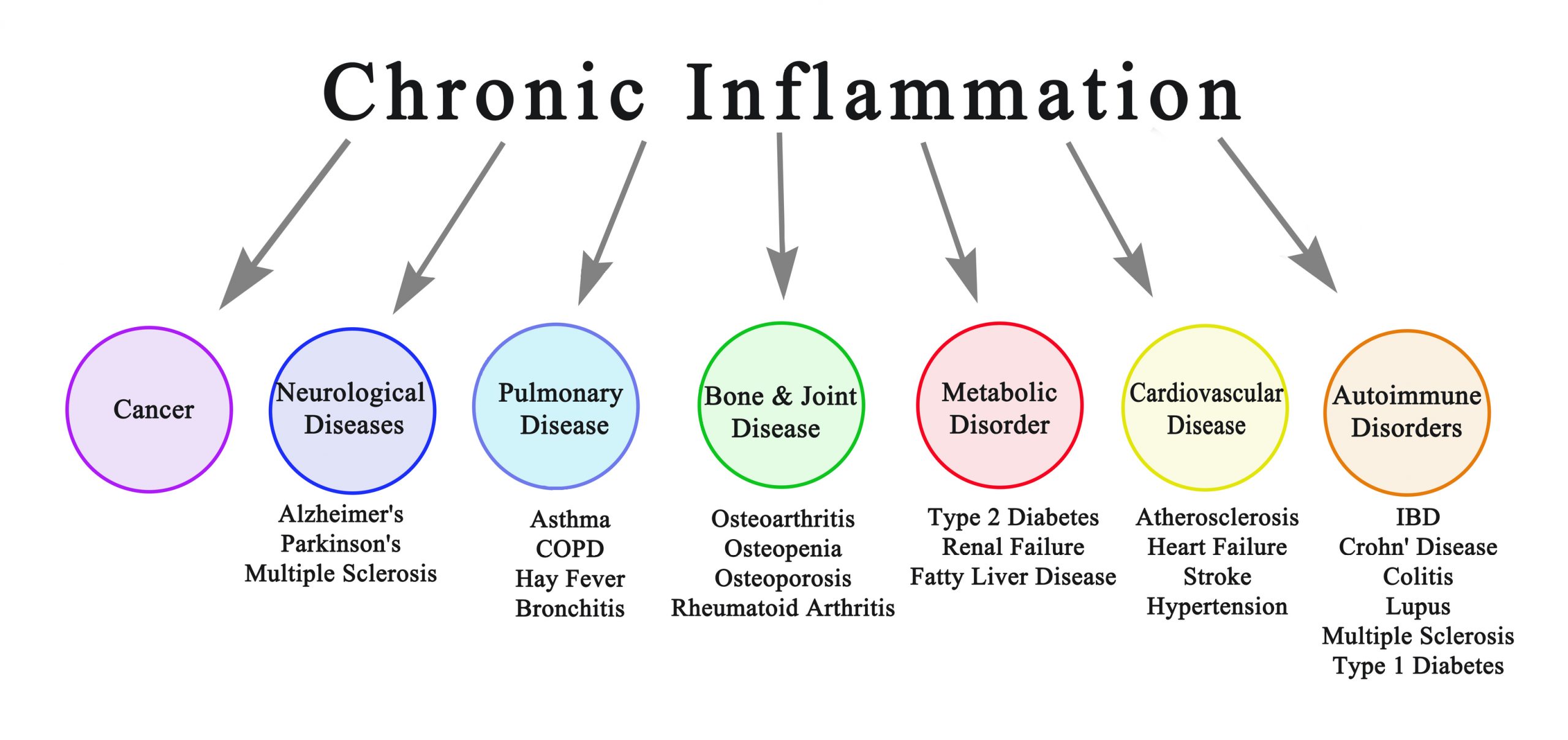
Most people are familiar with the inflammation that occurs when we injure a joint, cut ourselves or develop an infection. This swelling, redness, heat, and pain is one of our body’s most important mechanisms to heal an injury or fight infection. This acute inflammatory process generally lasts a few days and is the body’s way of recovering naturally. However, it is also possible to develop chronic, systemic inflammation, not related to injury or infection, which causes continual low-level inflammation throughout the body. This type of inflammation can result in damage to healthy tissue leading to many diseases, including osteoporosis.
Chronic inflammation has been found to be a culprit in a wide array of health conditions including cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, dementia, asthma, obesity and age-related macular degeneration. There is mounting evidence that suggests chronic systemic inflammation can also contribute to osteoporosis and increase the risk of fractures in aging adults.
Ongoing systemic inflammation may contribute to loss of bone mass and bone strength by affecting the bone remodeling process; the process where old bone is reabsorbed and new bone is laid down. Inflammation causes an increase in osteoclast activity (cells that break down bone) resulting in accelerated bone loss. Over time, this will lead to a decrease in bone mass leaving them weakened and more susceptible to breaking.
Chronic inflammation is generally not caused by a specific injury but things like:
-
Diet high in processed foods, sugar, trans fats
-
Smoking
-
Chronic stress
-
Poor sleep
-
Obesity
-
Unhealthy gut
-
Chronic infections
-
Toxins
What are some signs and symptoms that chronic inflammation may be contributing to your health issue?
-
Chronic body pains, arthritis, muscle pain
-
Constantly being tired or fatigued
-
Mood disorders like depression or anxiety
-
Memory issues or brain fog
-
Frequent colds and infections
-
Abdominal fat
-
Bowel issues
-
Skin rashes
-
Dry eyes
Testing to check for Chronic inflammation:
-
C-Reactive Protein (CRP): CRP levels increase in the blood when there is a condition causing inflammation.
-
Homocysteine: High levels of homocysteine can be linked to inflammation
-
Omega 3 fatty acids: Low levels of omega 3 fatty acids can contribute to inflammation
-
Anti-Oxidants: CoQ10, vitamins E, A and C are all powerful anti-oxidants that are needed to protect your cells against inflammation
There are many comprehensive tests available, beyond the common blood test, that can test for not only CRP and homocysteine but also for the important anti-oxidants and fatty acids
If you are interested, please reach out to me. susan@nurturedbones.com
Coming up next, lifestyle habits to help reduce and control chronic inflammation!
But in the meantime, I have put together an anti-inflammatory questionnaire that walks you through all of the different signs and symptoms of inflammation. You can use the questionnaire to rate your symptoms now and then again in 1-2 months from now after following an anti-inflammatory diet and lifestyle.
You can download the Inflammatory questionnaire/index HERE.